Monitoring
Enabling from the command line
-m, --http_port PORT HTTP PORT for monitoring
-ms,--https_port PORT Use HTTPS PORT for monitoring (requires TLS cert and key)nats-streaming-server -m 8222[19339] 2019/06/24 15:02:38.251091 [INF] STREAM: Starting nats-streaming-server[test-cluster] version 0.15.1
[19339] 2019/06/24 15:02:38.251238 [INF] STREAM: ServerID: 0Z2HXClEM6BPsGaKcoHg5N
[19339] 2019/06/24 15:02:38.251243 [INF] STREAM: Go version: go1.12
[19339] 2019/06/24 15:02:38.251862 [INF] Starting nats-server version 2.0.0
[19339] 2019/06/24 15:02:38.251873 [INF] Git commit [not set]
[19339] 2019/06/24 15:02:38.252173 [INF] Starting http monitor on 0.0.0.0:8222
[19339] 2019/06/24 15:02:38.252248 [INF] Listening for client connections on 0.0.0.0:4222
(...)Enabling from the configuration file
Monitoring a NATS Streaming channel with Grafana and Prometheus
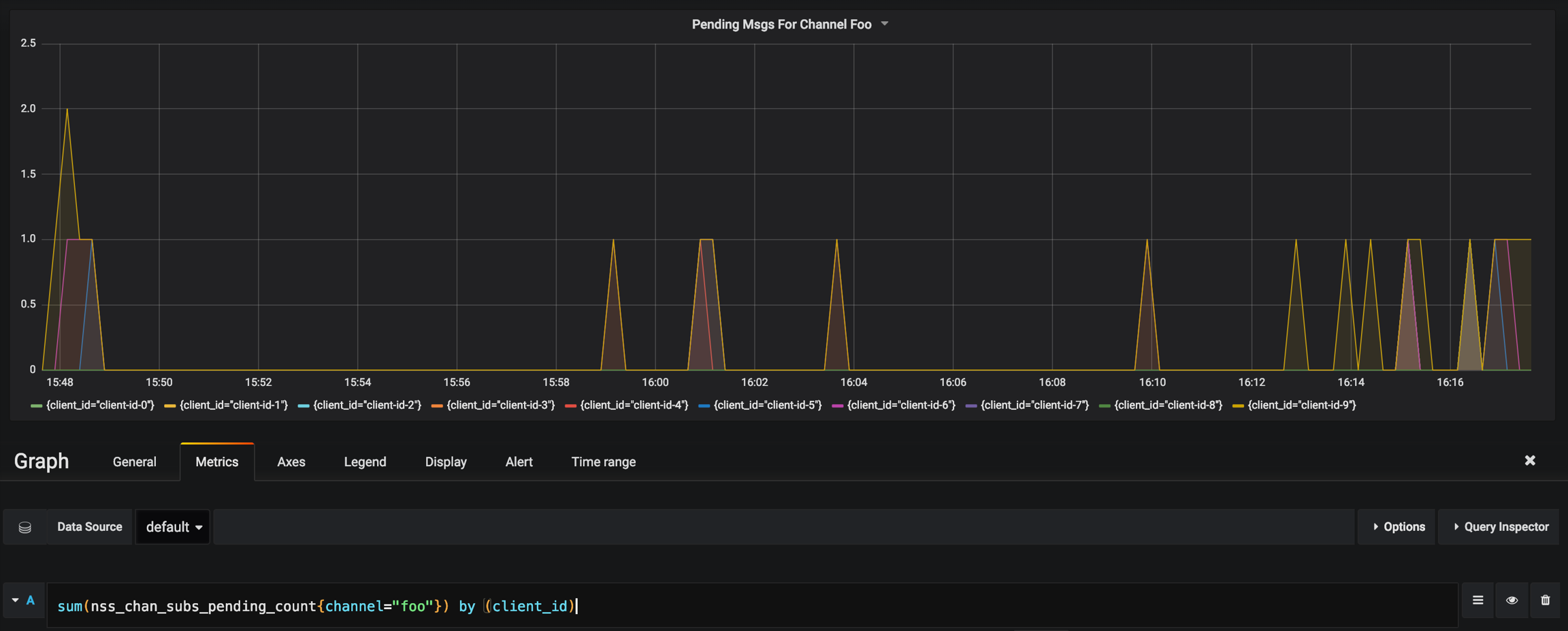
Pending Messages from Channel Foo
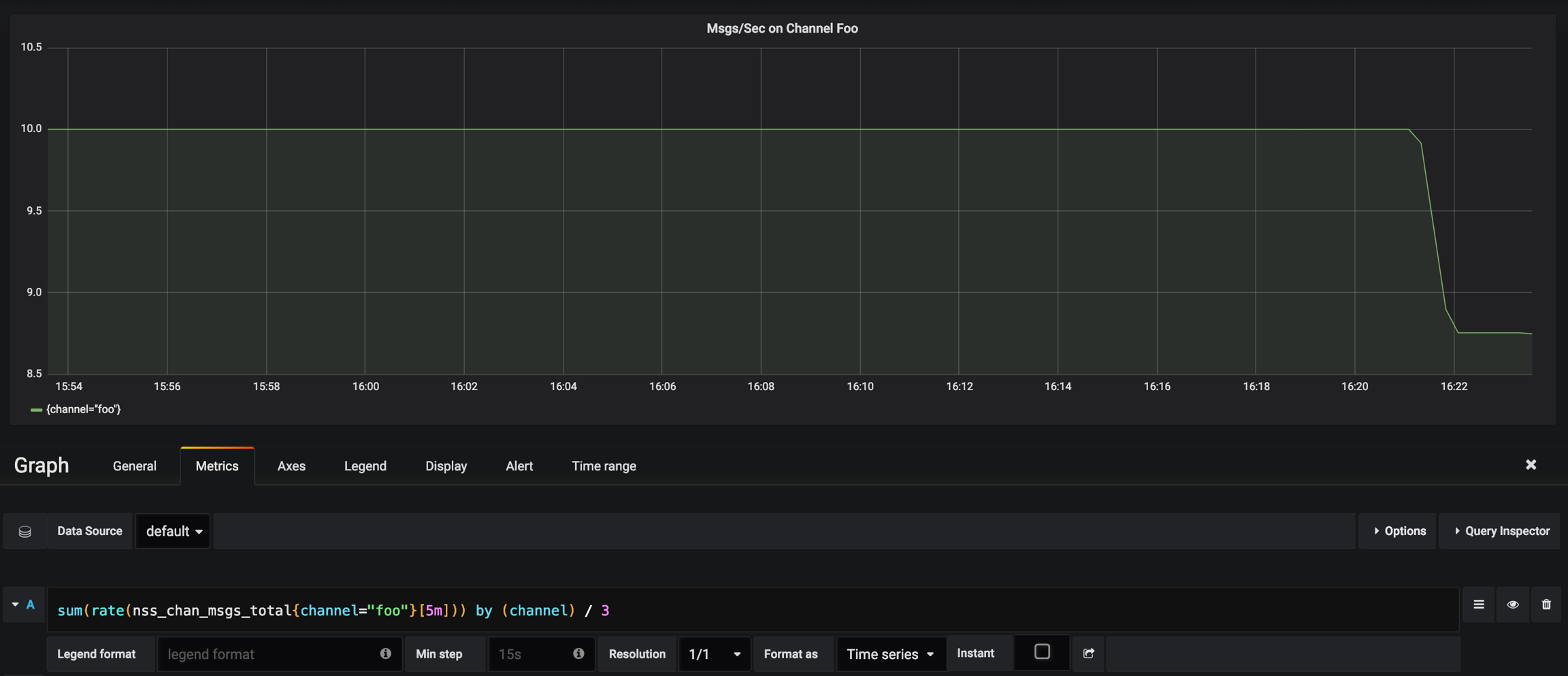
Messages Per Sec Delivered on Channel Foo
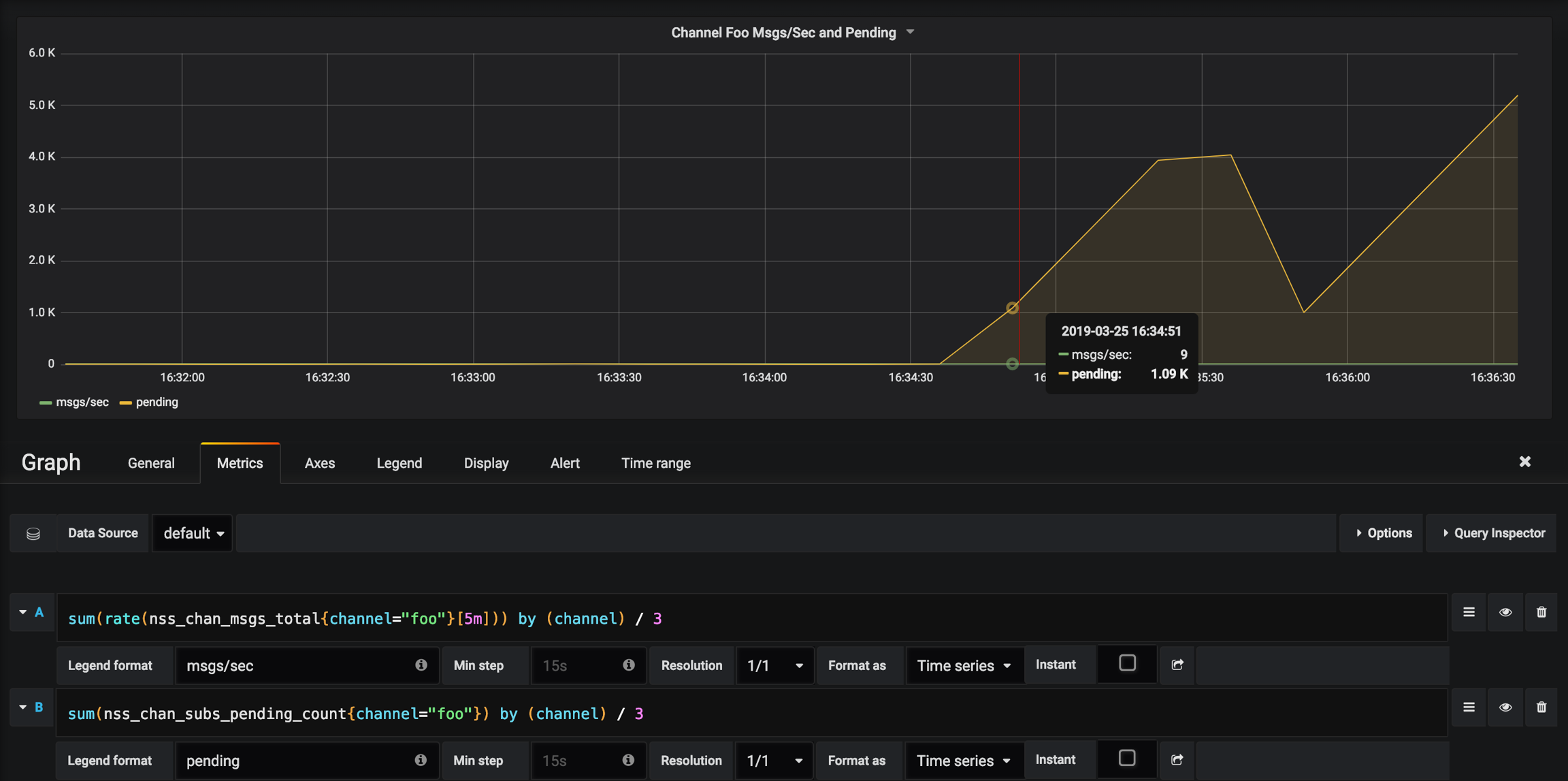
Msgs/Sec vs Pending on Channel
最后更新于